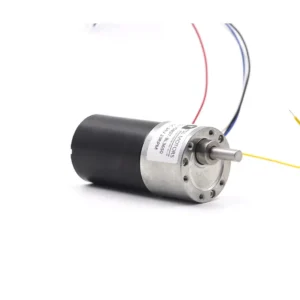
Choosing a high torque dc motor is crucial for success in industrial automation, robotics, and heavy-duty applications. The high torque dc motor is the device’s “heart,” determining system efficiency, stability, and service life.
Are you often confused by these critical choices when selecting a high torque dc motor for your project?
- 12V or 24V?
- Brushed vs. Brushless?
- Which gearbox structure is best?
With over 15 years of manufacturing experience, TSL MOTOR understands the importance of these decisions.
In this article, we provide a manufacturer-level internal insight, deeply analyzing the principles and structures of 12V/24V high-torque DC motors, and comparing the pros and cons of BLDC.
Key Takeaways
- Voltage Stability. The 24V system uses lower current, leading to less heat generation. This results in more stable torque output and longer life.
- Gearbox Power. For high torque output in a compact space, the planetary gearbox is the best option. It provides the highest torque density for heavy-duty applications.
- DC/BLDC Trade-off. Choose Brushed DC for strong instantaneous starting force and lower cost. Select BLDC for superior longevity, efficiency, and quiet operation.
- Duty Cycle. If the equipment runs for a long duration, prioritize 24V and BLDC to manage heat and wear. If the run time is short, 12V DC may suffice.
- Safety Margin. Never size the motor exactly to the requirement; this leads to frequent failure. Use an engineering safety factor, ensuring the chosen torque is at least 1.5 times the required load.
Why High Torque DC Motors Are So Critical
When working on a project, the main concern is often not the motor’s speed but whether it can actually “push the load and lift the weight.” High torque dc motors have several practical engineering roles:
(I) Ability to Drive the Load
Insufficient motor torque leads to these troubles:
- Starting Difficulty: The device stalls right at startup; the motor hums but doesn’t turn.
- Unstable Operation: It vibrates heavily under a large load, making precision impossible.
- Overheating Shutdown: Prolonged overloading causes temperature spikes, tripping the protection circuit.
- Shortened Service Life: Windings, bearings, and carbon brushes fail prematurely.
Conclusion: Insufficient torque means the equipment simply cannot run.
(II) Efficiency and Stability
A motor with ample torque runs much easier:
- Stress-Free Low-Load Operation: The motor doesn’t have to strain, leading to less wear and a longer life.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Lower current pressure, less heat generation, and higher overall efficiency.
- Higher System Reliability: Stable torque on automated lines or robots means less downtime and maintenance.
This is why many factories prefer high torque DC motors, even at a higher cost.
(III) Size and Cost of the Transmission System
High torque density motors also offer the advantage of a more compact system:
- Smaller Motor Size: Solving the problem with less volume for the same torque.
- Lower Required Gear Ratio: One less gear stage means higher efficiency and lower noise.
- Reduced Overall Cost: Simpler structure naturally lowers manufacturing and maintenance costs.
Choosing the wrong motor often means redesigning the entire mechanical structure—a disaster for the project.
High Torque DC Motor: 12V vs. 24V
High torque DC motors matter. They move the load, keep systems stable, cut transmission size. But picking the motor isn’t enough — the real trick is choosing the right voltage.
Many people think voltage is just a power specification, but in high-torque motor applications, voltage choice profoundly impacts the entire system’s performance. It relates to:
- Starting Torque Magnitude
- Current and Thermal Management
- Cost and Wiring Harness Design
- Controller Compatibility
- Long-term System Stability and Reliability
Understanding the engineering significance of voltage differences is key to making the correct selection.
Impact of 12V VS 24V on High Torque DC Motor Performance
Comparison based on the same power output.
Table 1:Impact of 12V VS 24V on High Torque DC Motor Performance
| Item | 12V System | 24V System |
| Inrush Current | High (Approx. 2× of 24V) | Low, easier to manage |
| Copper Loss / Thermal Stress | High (Large I²R loss) | Low, higher efficiency |
| Torque Stability | Medium; strongly affected by heat | Stable; less thermal degradation |
| Wiring Loss | High; requires thicker wires | Low; thinner wires reduce cost |
| Motor Life Impact | Higher temperature → shorter life | Lower temperature → longer life |
| Controller Cost | Low (12V options are common) | Slightly higher; better for industrial control |
| System Noise | Higher current → slightly more noise | Lower current → quieter |
| Typical Applications | Vehicle systems, power-limited mechanisms | Industrial equipment, robotics, long-duration systems |
Why is 12V “Strained” at the Same Power?
- Power Formula: P = U × I
- Example: For the same 120W output:
- 12V System requires 10A
- 24V System only requires 5A
The doubled current causes problems: More heat generation in wires (I²R loss increases exponentially). Controller needs larger MOSFETs and stronger heat dissipation. Higher temperature rise in motor windings. Faster wear of the commutation system in brushed motors.
Therefore, in high-torque, long-running equipment, 12V motors often suffer from excessive temperature rise, leading to: torque drop, unstable speed, shortened life, and performance decay over time.
Why Heavy Loads Prefer 24V?
More Stable Torque Output (Especially Continuous Torque) A 24V motor, for the same volume, can achieve lower current → lower temperature rise → more stable magnetic field.
Engineering Significance: Continuous operation is unaffected by temperature on torque. Peak torque capacity is maintained longer. More reliable for frequently starting/stopping equipment (e.g., AGVs, grippers).
A.Better Wiring Harness Design (Saves Cost and Space) In automation equipment:
- Thicker cables are harder to route.
- Higher current requires more consideration for voltage drop.
- Harness cost, weight, and installation difficulty all increase. The 24V system’s current is half that of 12V, directly simplifying the overall machine design.
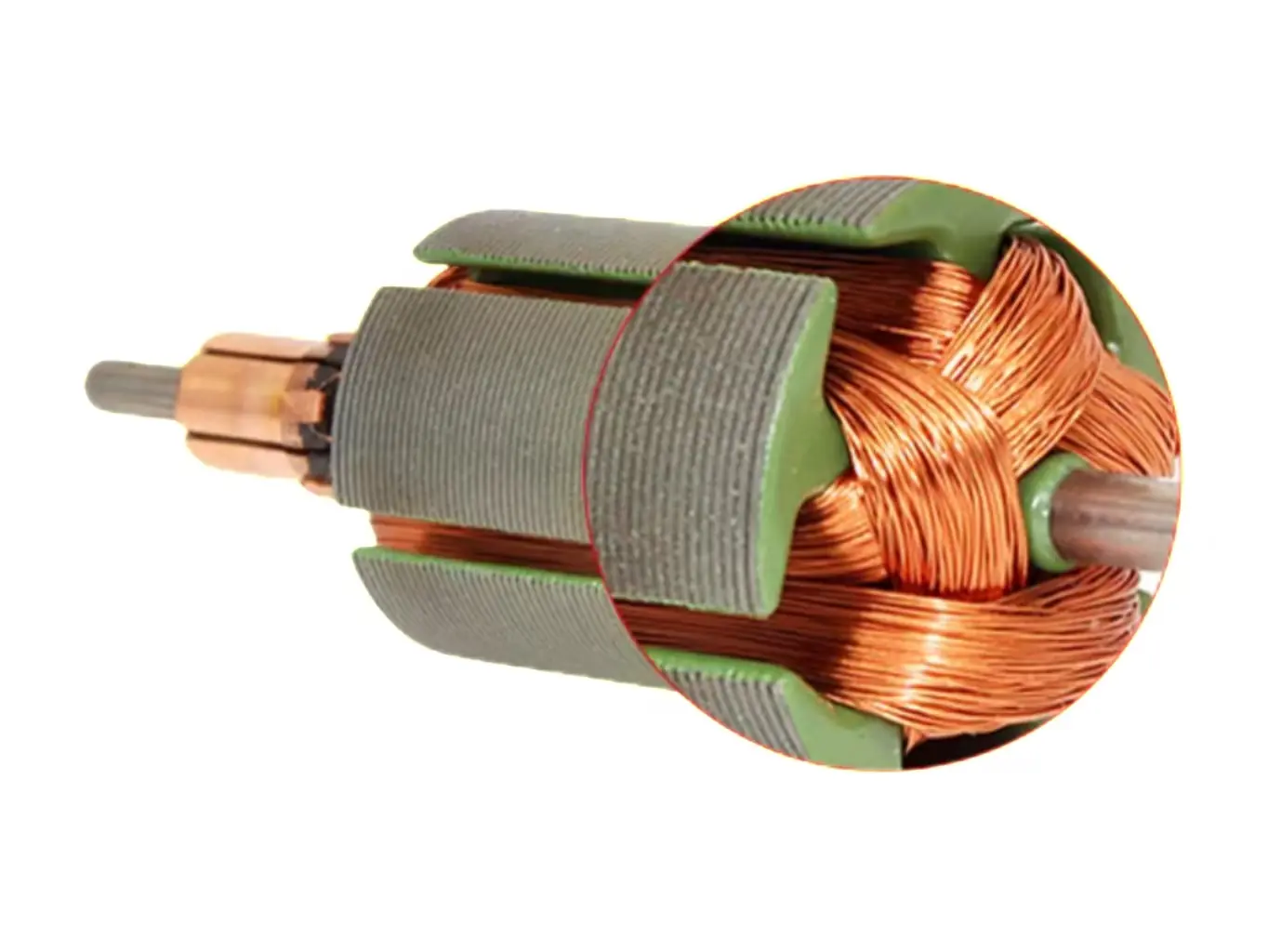


B. Easier Controller Stabilization (Lower Thermal Load) The controller’s MOSFET or H-bridge current load is halved, meaning:
- Lower temperature
- Longer component life
- Easier EMC compliance
- Lower failure rate
For this reason, industrial-grade BLDC controllers almost universally adopt the 24V system.
When is 12V Necessary?
The following scenarios usually require 12V:
- Vehicle Systems (Cars, RVs, Ships) The vehicle power system is 12V and must be compatible.
- Power-Restricted or Portable Devices Such as handheld tools, small pumps, and portable equipment.
- Low Torque, Small Volume, Short-Time Operation Designs 12V is easier to find compatible power supplies for, and the cost is lower.
Final Selection Formula
If you need: High Torque, Continuous Operation, Low Noise, Long Life, Stable Output ➡️ Prioritize 24V
If your design is: Power-Restricted, Cost-Sensitive, Very Small Volume, Short Duty Cycle ➡️ 12V is more reasonable
BDC vs. BLDC: Which is Better for High Torque Projects?
For an engineer, even after deciding between 12V and 24V, there’s still another dilemma: should I go with a high torque brushed DC motor or a brushless one?They differ significantly in structure, performance, and application scenarios.
High Torque Brushed DC Motor
Principle: Current is fed to the rotor windings via brushes and a commutator. The resulting electromagnetic field interacts with the stator field to create torque. The commutator continuously switches the current direction for continuous rotation.

- Pros:
- Strong Instantaneous Torque: Large starting torque, ideal for scenarios requiring “instant burst force,” like vehicle lifts and industrial grippers.
- Low Cost: Simple structure, with cost advantages in manufacturing and procurement.
- Simple Control: Requires only PWM drive, no complex drivers or control algorithms.
- Flexible Customization: Windings, magnets, and gear ratios can be quickly adjusted.
- Typical Applications: Heavy-duty yet cost-sensitive equipment, such as automotive aftermarket systems, small machinery, and portable devices.
Engineer’s Tip: If the project budget is limited and requires strong starting power, the high torque brushed dc motor is often the first choice.
High Torque Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)
Principle: An electronic drive circuit controls the energizing sequence of the stator windings to create a rotating magnetic field, which interacts with the permanent magnet rotor to produce torque and achieve continuous rotation. Electronic commutation replaces mechanical brushes, resulting in higher efficiency and longer life.

- Pros:
- Higher Torque Density: Can output greater torque for the same volume, suitable for space-constrained devices.
- Long Life: No brush wear, reliability and lifespan far exceed DC motors.
- High Efficiency: Electronic commutation reduces energy loss, leading to better overall efficiency.
- Lower Noise: Runs smoothly, especially suitable for noise-sensitive scenarios like medical devices and robotics.
- Typical Applications: Long-cycle operation, high-end equipment, automated production lines, and medical devices.
Engineer’s Tip: If the equipment requires long-term stable operation, or space is limited, the BLDC is more appropriate.
High Torque DC Motor:BDC VS BLDC Performance Comparison
Table 2:High Torque DC Motor:BDC VS BLDC Performance Comparison
Table 2:High Torque DC Motor:BDC VS BLDC Performance Comparison
| Performance Metric | DC Brushed Motor | BLDC Brushless Motor |
| Torque Stability | Medium | High |
| Starting Impact Force | Strong | Medium |
| Life | Medium | Extremely High |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
| Control Complexity | Simple | Requires a driver |
| Noise | Higher | Low |
Seeking Starting Impact Force + Cost-Effectiveness → DC is suitable for heavy-duty, budget-constrained scenarios requiring instant high torque.
Seeking High Power Density + Long Life + Quiet Stability → BLDC is suitable for high-end equipment, long-cycle operation, and space-constrained systems.
Which Gearbox Structure is Best for High Torque DC Motors?
I know I’ve already decided between 12V and 24V, and between brushed or brushless motors, but I’m still unsure how to choose the gearbox structure. Simply put, if high torque is the goal, a planetary gearbox is almost the only suitable option.
Spur Gearbox
The spur gearbox uses the most common and simple reduction method: reducing the motor’s high speed to gain higher torque using straight-cut gears.
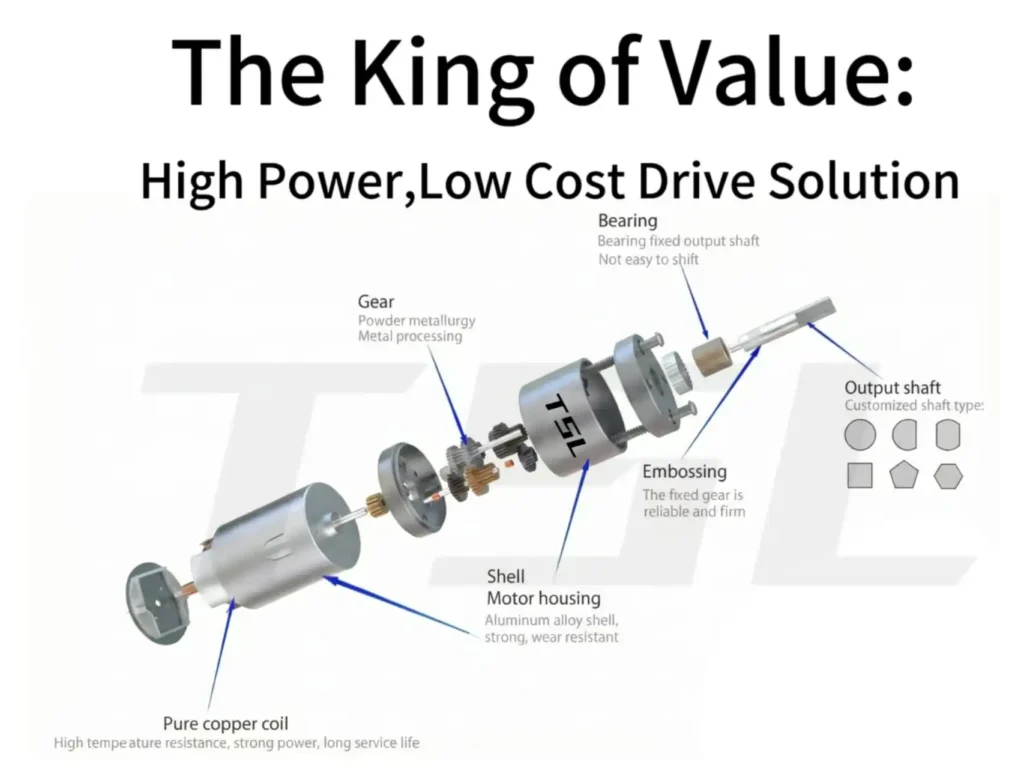
Pros: Simple structure, high efficiency, small size, low cost—very economical.
Cons: High noise, limited load capacity; typically used only in home appliances, small machinery, or cost-sensitive light-duty scenarios.
Planetary Gearbox
The planetary gearbox is the “high-performance candidate” in engineers’ eyes. It uses a combination of a sun gear, planet gears, and a ring gear to distribute torque. Multiple planet gears engage simultaneously, resulting in even load distribution and extremely high torque density.
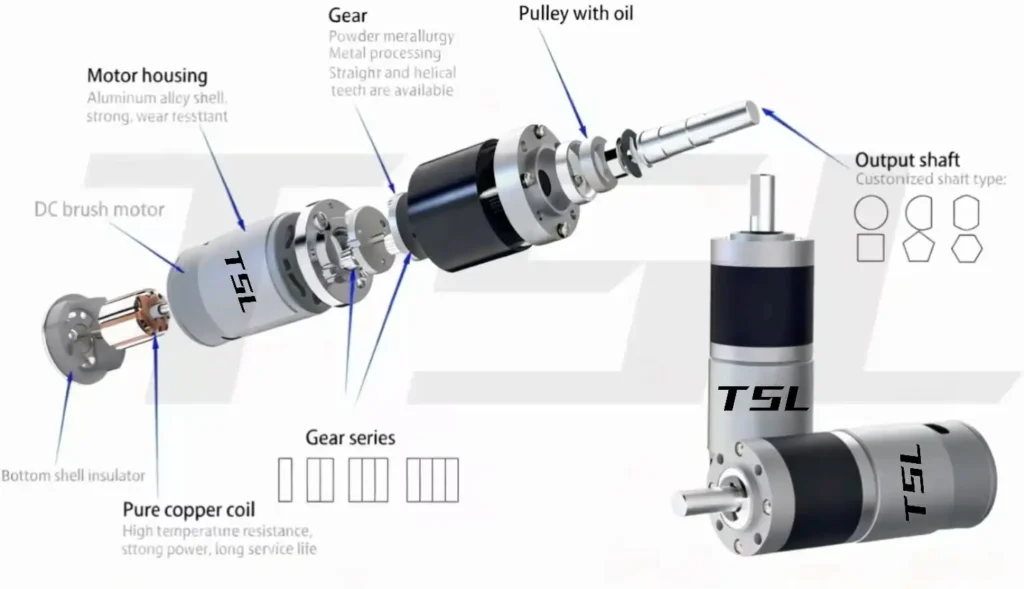
Pros: Small size, high efficiency, low backlash; provides powerful force in a compact space.
Cons: Higher cost than spur gears, but it is the near-standard for high-performance applications like robotics, automation equipment, and medical devices.
Worm Gearbox
The worm gearbox‘s biggest feature is self-locking. The worm can easily drive the worm wheel, but the worm wheel can hardly drive the worm in reverse. This makes it particularly useful in lifting systems, automatic doors, and medical equipment—preventing back-driving without an external brake.
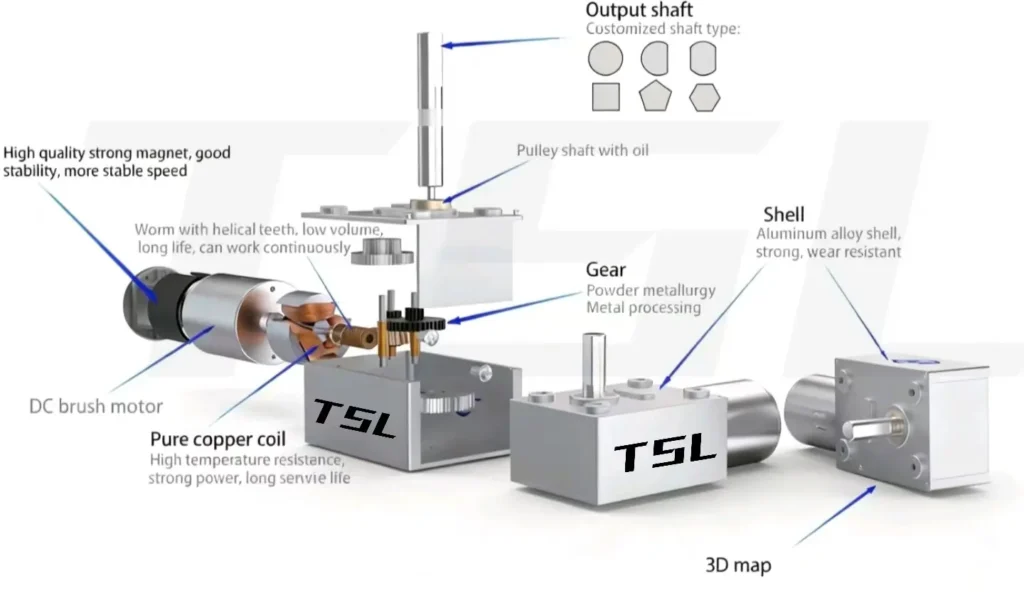
Pros: Low noise, stable operation, decent torque output.
Cons: Lower efficiency than planetary gears, and generally larger volume.
Simple Comparison of Three Common Gearbox Types
Table 3:simple Comparison of Three Common Gearbox Types
| Type | Torque Capacity | Noise | Volume | Cost |
| Spur | ★★ | Noisy | Small | Low |
| Planetary | ★★★★★ | Medium | Small | High |
| Worm | ★★★★ | Low | Large | Medium-High |
Engineer’s Conclusion:
If the goal is high torque output, the planetary gearbox is virtually the only suitable solution. It provides extremely high torque density in a limited space while remaining compact, making it the top choice for high-load scenarios like robotics, AGVs, and medical devices.
The worm gearbox is better suited for situations requiring quiet operation and self-locking, such as vehicle lifting mechanisms. The spur gearbox, while cheap, is often underpowered for heavy loads.
TSL MOTOR’s High Torque DC Motor Solutions
TSL MOTOR has over 15 years of precision motor manufacturing experience, forming a mature design system and customization capability in the high torque DC motor field. Our products not only meet standard applications but can also be deeply optimized according to customer needs.
Core Design Advantages
Powerful Magnetic Tiles: Strong magnetic tiles maintain low noise, high torque, and long life over a wider voltage range.

Pure Copper Coils: Made with high-quality materials for a one-piece rotor, ensuring high conductivity, long wear life, high-temperature resistance, and stable speed.
High-Quality Carbon Brushes: Optimized brush-commutator contact structure to reduce energy loss and improve reliability and lifespan.

Low Noise Imported Bearings: Uses high-precision Japanese bearings to reduce friction between rollers and bearing walls, leading to higher speed, less heat generation, higher load resistance, and resistance to discoloration/rusting.
Metal Powder Metallurgy Gears / CNC Precision Gears: Enhances gearbox wear resistance and transmission efficiency, suitable for long-term heavy-duty operation.

Custom Torque Platforms: Covers a wide range of application scenarios from light to heavy load.
Voltage Platform Selection
Whether high torque brushed dc motor or high torque bldc motor, TSL MOTOR can customize the voltage platform according to customer requirements:
- 12V High Starting Torque Series: Suitable for vehicle equipment, portable machinery, and small smart appliances requiring instant high torque.
- 24V High Stable Torque Series: Suitable for industrial automation, robotics, and AGV/AMR devices requiring long-term operation.
- BLDC High Power Density Series: Suitable for high-end robotics, medical devices, and other space-constrained applications demanding high efficiency and long life.
Customization Capability
TSL MOTOR provides flexible customization options to ensure a perfect match between the motor and the system:
Custom Gear Ratios: Selecting the optimal reduction solution based on load characteristics.
Custom Torque Output: Meeting the torque demands for different operating conditions.
Controller and Hall Configuration: Supporting open-loop/closed-loop control and compatible with various drive methods.
With Encoder (Position/Speed Feedback): Suitable for automation and robotic systems requiring precise control.
Various Shaft Designs: Supporting D-shaft, threaded shaft, long shaft, and other structures for easy integration with customer mechanical systems.
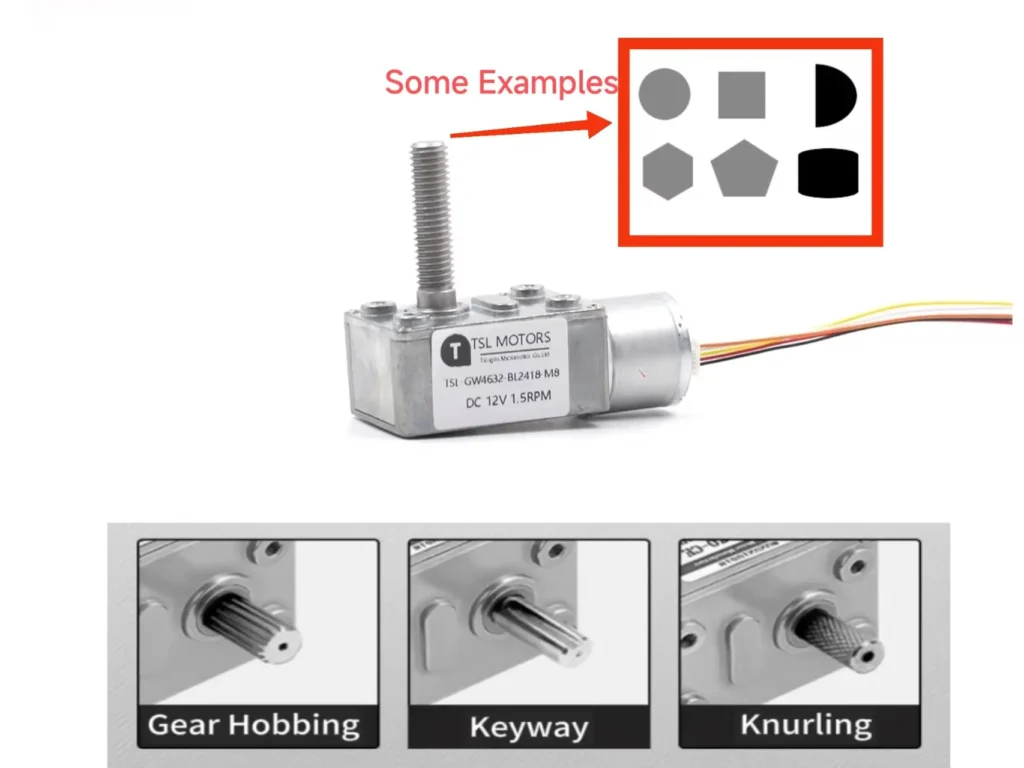

High Torque DC Motor Applications
Case 1: AGV/AMR Drive Wheel
Original Problem: Small motors lacked sufficient torque when large AGVs climbed slopes, resulting in slow climbing speed or even stalling.
Solution: Adopting a 24V micro DC motor + Planetary Gearbox to increase the motor’s torque density.



Results: Torque increased by 42%, effectively solving the problem of insufficient climbing power. Motor temperature rise decreased by 15°C, extending continuous operation life. Overall system efficiency improved, increasing battery life by about 12%.
Case 2: Industrial Gripper System
Original Problem: Gripping force fluctuated and movement stalled, affecting production precision and cycle time.
Solution: Adopting a micro BLDC motor + Encoder closed-loop control to achieve precise position and torque feedback.

Results: Repeatability improved to ±0.3°, resulting in smoother gripping action. Gripping force stability increased by 30%, reducing workpiece slippage. System noise reduced, making it suitable for quiet production environments.
Case 3: Vehicle Lifting Structure
Original Problem: Instantaneous load was too high, with strict noise requirements simultaneously.
Solution: Adopting a 12V high starting torque micro DC motor + Worm Gear structure, balancing starting torque and self-locking characteristics.



Results: Faster instantaneous load response; smoother lifting and lowering actions. Noise reduced by 25%, meeting the comfort requirements of the vehicle environment. Reliability significantly improved, with Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) extended by about 20%.
Summary
In engineering projects, motor selection is never just a matter of comparing parameters. It requires decisions based on the application scenario, load characteristics, and overall system goals. The guiding logic can be summarized clearly:
- If the need is stable torque over long periods, choose 24V. Lower current and reduced heat generation make it ideal for industrial equipment and robotics.
- If the need is strong starting impact force, choose a brushed DC motor. Its high starting torque and instant burst power suit vehicle lifts and grippers.
- If the need is long life, low noise, and high power density, choose a BLDC motor. With no brush wear, it offers high efficiency and reliability, perfect for medical devices, automated production lines, and high-end robotics.
- If the need is very high torque, choose a planetary gearbox. Its compact design delivers extreme torque density, making it the go-to for heavy-load applications.
- If the need is high reliability, ensure the motor torque is at least 1.5 times the requirement. Without this safety margin, failures become frequent.
- If the need is to reduce R&D time,consult with engineers. Motor selection is not just parameter matching but system optimization, and expert guidance avoids pitfalls and accelerates development.
FAQ
Q1: Why are high torque dc motors critical?
A: They can drive heavy loads, increase system efficiency and stability, and allow for a more compact system design.
Q2: Which is better: 12V or 24V?
A: 24V is generally better. It has lower current, less heat, more stable torque, and longer life, suitable for industrial continuous operation.
Q3: How do I choose between DC (Brushed) and BLDC (Brushless)?
A: DC is suited for: strong starting impact force and low cost.
BLDC is suited for: long life, high efficiency, and quiet operation.
Q4:Which gearbox structure is best for high torque?
A: The Planetary Gearbox. it provides the highest torque density in a limited space.
TSL MOTOR Products
-
 DC Gear Motor126 products
DC Gear Motor126 products-
 6mm Planetary Gear Motor4 products
6mm Planetary Gear Motor4 products -
 6mm Planetary Metal Gear Motor3 products
6mm Planetary Metal Gear Motor3 products -
 Brushless Gear Motor15 products
Brushless Gear Motor15 products -
 Micro Gear Motor62 products
Micro Gear Motor62 products-
 Coreless Gear Motor11 products
Coreless Gear Motor11 products -
 N20 Gear Motor26 products
N20 Gear Motor26 products -
 Plastic Gearbox Motor8 products
Plastic Gearbox Motor8 products -
 Standard Gear Motor15 products
Standard Gear Motor15 products -
 Stepper Gear Motor13 products
Stepper Gear Motor13 products
-
-
 Planetary Gear Motor25 products
Planetary Gear Motor25 products -
 Spur Gear Motor60 products
Spur Gear Motor60 products -
 Worm Gear Motor23 products
Worm Gear Motor23 products
-
-
 DC Motor78 products
DC Motor78 products-
 Brushed DC Motor16 products
Brushed DC Motor16 products -
 Brushless DC Motor21 products
Brushless DC Motor21 products -
 Coreless DC Motor13 products
Coreless DC Motor13 products -
 Micro DC Motor15 products
Micro DC Motor15 products -
 Stepper Motor13 products
Stepper Motor13 products
-
-
 Vibration Motors67 products
Vibration Motors67 products-
 Brushless Vibration Motor8 products
Brushless Vibration Motor8 products -
 Coin Vibration Motor19 products
Coin Vibration Motor19 products -
 Coreless Vibration Motor3 products
Coreless Vibration Motor3 products -
 Encapsulated Vibration Motor6 products
Encapsulated Vibration Motor6 products -
 Linear Resonant Actuator8 products
Linear Resonant Actuator8 products -
 Powerful Vibrating Motor17 products
Powerful Vibrating Motor17 products -
 SMD Vibration Motor4 products
SMD Vibration Motor4 products -
 Sonic Vibration Motor2 products
Sonic Vibration Motor2 products
-