As the automotive industry moves toward intelligence, comfort, and electrification, the HVAC system has changed. It is no longer just a temperature regulator. It is now a complex electromechanical system. It manages heat, air quality, and cabin environment.
The damper actuator is the key part. It converts ECU commands into airflow control. Early cars used cables or vacuum diaphragms. Precision was low. Automation was difficult. With automatic climate control, electric actuators became essential.
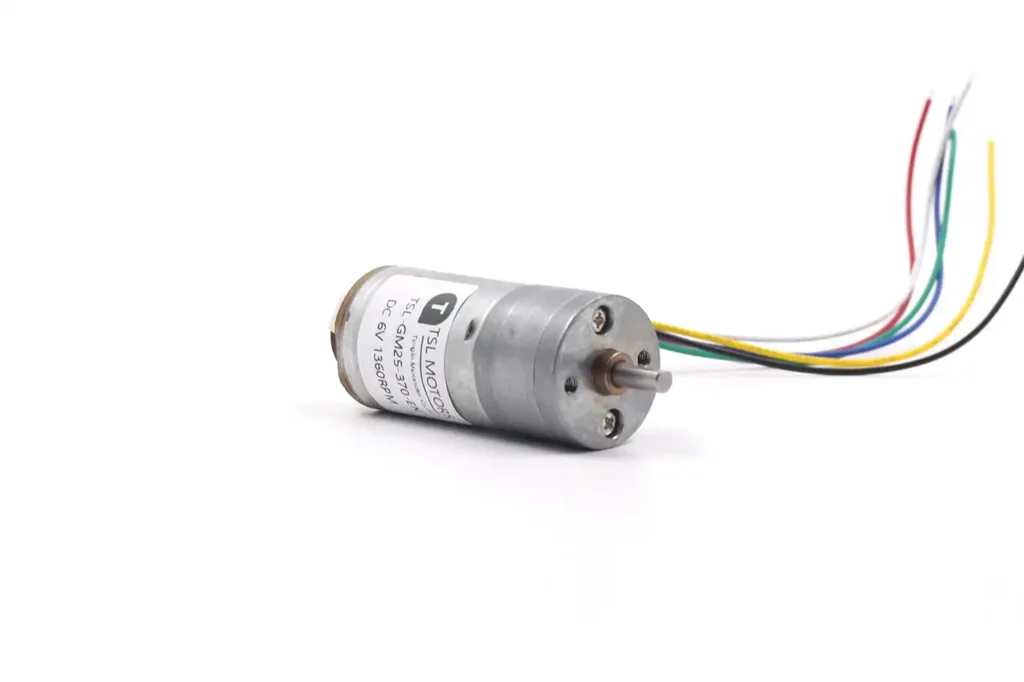
The TSL-RS-370 DC motor is the core driver. It affects response speed. It ensures accurate positioning. It reduces noise. Custom designs for 5V, 6V, 12V, and 24V match different applications.
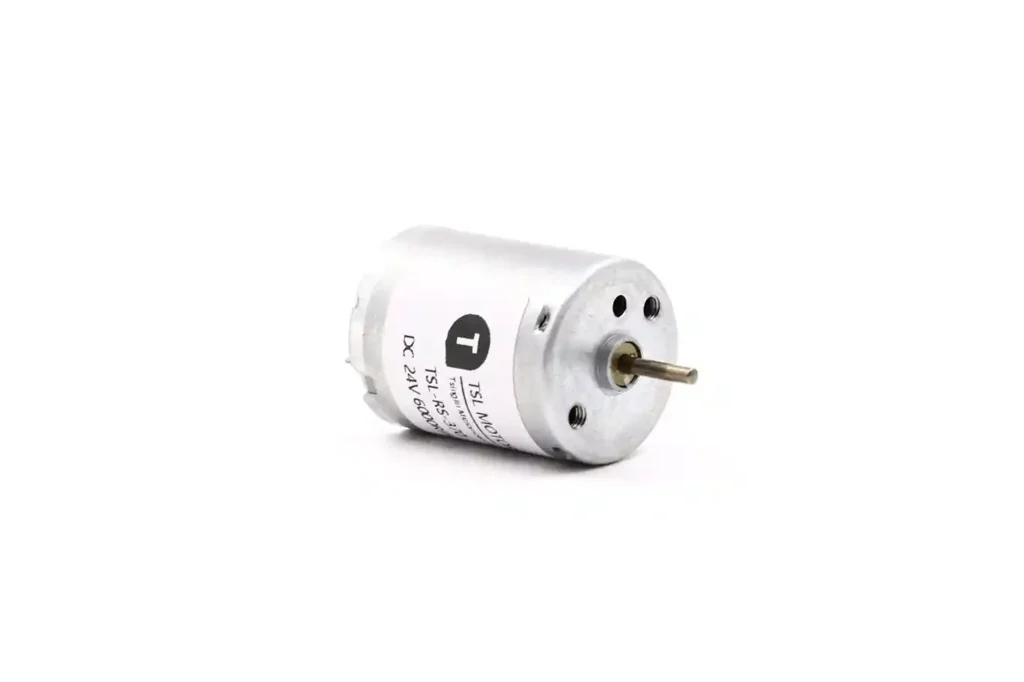

We are a leading DC motor manufacturer in China. We provide one-stop custom solutions. This report analyzes damper actuators. It covers electromagnetics, control algorithms, materials, and NVH. It also looks ahead to smart cockpits and NEV thermal management.
Key Takeaways
- Definition and Core Purpose The damper actuator is an electromechanical device. It translates electronic ECU commands into physical mechanical motion. Its core role is to precisely manage the airflow path, temperature, and direction within the HVAC unit.
- Key Internal Components The actuator primarily consists of the drive motor, a multi-stage reduction gearbox, and a position feedback sensor. The motor provides power, the gearbox amplifies torque, and the sensor feeds angle information to the ECU.
- Mechanism for Temperature Control The Blend Door actuator drives a flap to regulate the airflow passing over the heater core. This achieves stepless mixing of hot and cold air to reach the desired outlet temperature.
- Mechanism for Airflow Direction The Mode Door actuator utilizes linkages or cam mechanisms to move multiple air flaps. This accurately switches the airflow between face, foot, and defrost outlets.
- Stability and Self-Locking The actuator’s reduction gearbox frequently incorporates a worm gear design. This mechanism provides natural “self-locking” capability, ensuring the door is not displaced by high-speed airflow.
Automotive HVAC System Architecture and Damper Control Principles
To understand the operating environment of a damper actuator, one must first analyze the fluid dynamics and thermodynamic architecture of the HVAC assembly.
The HVAC Unit is typically located under the dashboard and is an assembly containing a blower, evaporator, heater core, and a complex network of air ducts.
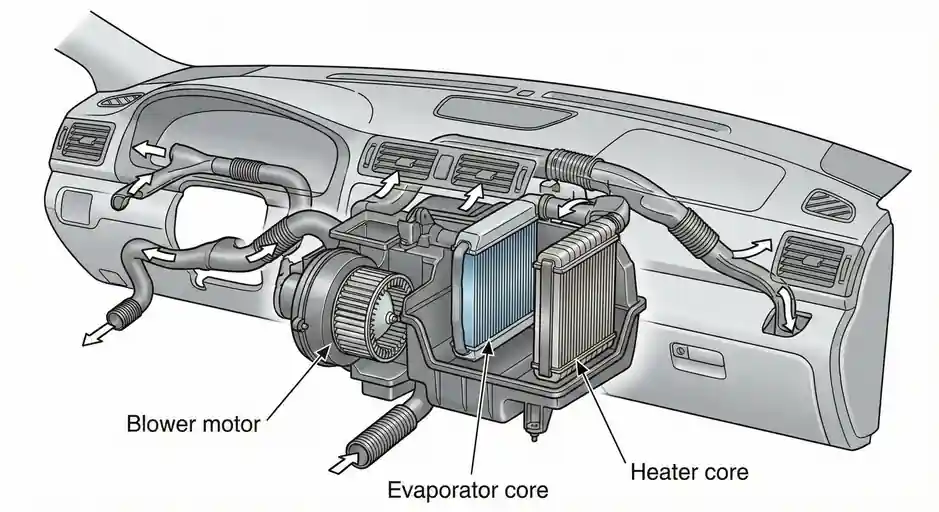
Airflow Management Logic and Actuator Classification
Damper actuators are primarily divided into three categories based on their controlled functions, each imposing specific torque and speed requirements on the motor:
Intake/Recirculation Damper Actuator
This actuator controls the ratio of Fresh Air to Recirculated Air.
Working Principle: Typically switches between two limit positions (“Full Open” and “Full Closed”) and rarely requires an intermediate position.

Control Logic:
Rapid Defrost: In cold weather, the system forces a switch to external circulation to introduce dry air, using the AC evaporator to dehumidify and prevent windshield fogging.
Max A/C: In the initial phase of hot weather startup, the system switches to internal circulation to reduce thermal load and increase cooling speed.
Air Quality Management: In vehicles equipped with an Air Quality Sensor (AQS), when excessive external CO or NOx concentrations are detected (e.g., inside a tunnel), the actuator must close the intake within seconds. This places high demands on the transient response of the TSL-RS-370 motor.
Air-Mixing/Blend Door Damper Actuator
This is the most frequently working and highest precision actuator in the system.
Working Principle: It controls the proportion of airflow passing through the heater core, thereby regulating the outlet temperature.

Control Logic: The blend door requires stepless regulation from 0% to 100%. In automatic mode, algorithms constantly fine-tune the blend door position based on cabin temperature sensors, sunload sensors, and the set temperature.
Technical Challenges: Due to the physical mixing of hot and cold airflow, the aerodynamic resistance on the door is non-linear. The TSL-RS-370 motor must provide sufficient Stall Torque to overcome wind pressure while maintaining low noise.
Mode Distribution Damper Actuator
This actuator determines the direction of airflow: Face, Floor, Defrost, or combination modes.
- Working Principle: Multiple flaps are driven simultaneously via complex cam mechanisms or linkages.
- Control Logic: Mode switching usually involves long mechanical travel and high friction loads because one actuator may need to drive two or three air flaps simultaneously.
Fluid Dynamics Challenges in Damper Actuator
When the blower operates at high speed, the static pressure within the ducts increases significantly. The damper faces immense dynamic pressure on the windward side, requiring the actuator to possess “Self-Locking“ capability—meaning the damper must not be displaced by airflow when the motor is powered off.
This is typically achieved through a high-reduction worm gear mechanism, but it also requires the motor itself to possess a certain degree of Cogging Torque or braking torque.
Deep Technical Analysis of the TSL-RS-370 Series Motor
Our motor features a standard 24.3mm diameter housing design, a length of 30.8mm, and a 2mm shaft diameter, categorizing it as a typical precision micro DC brushed motor.
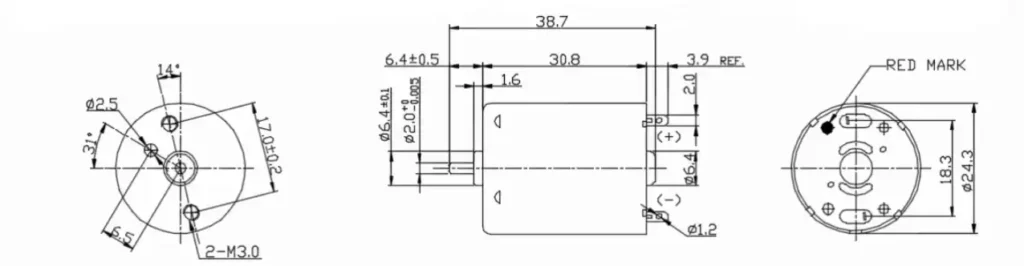
Key Performance Indicators Deep Dive
| Motor Model | Voltage | No Load | At Maximum Efficiency | Stall | |||||
| Current | Speed | Current | Speed | Torque | Output | Current | Torque | ||
| V | A | RPM | A | RPM | g.cm | W | A | g.cm | |
| TSL-RS-370CHV-25145 | 5 | 0.059 | 5495 | 0.38 | 4763 | 26.63 | 1.3 | 2.47 | 199.91 |
| TSL-RS-370CHV-18202 | 6 | 0.056 | 4424 | 0.28 | 3687 | 25.00 | 0.95 | 1.4 | 150.07 |
| TSL-RS-370CHV-20140 | 6 | 0.055 | 7300 | 0.36 | 6280 | 21.6 | 1.388 | 2.24 | 154 |
| TSL-RS-370CHV-11630 | 12 | 0.01 | 3183 | 0.05 | 2674 | 15.34 | 0.42 | 0.30 | 95.89 |
| TSL-RS-370CHV-10680 | 24 | 0.018 | 5000 | 0.11 | 4313 | 32.18 | 1.43 | 0.69 | 234.21 |
The Trade-off Between Voltage and Winding Design
We adapt to different voltage and performance needs by altering winding turns and wire diameter across different models.
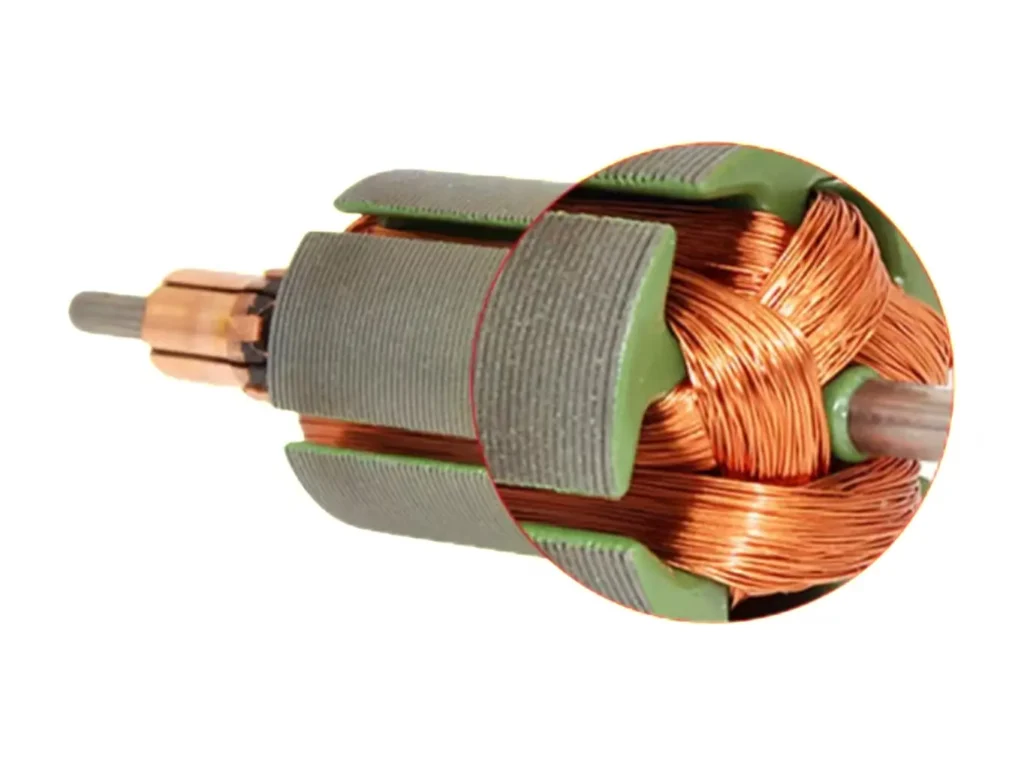

High Voltage vs. Low Current: The 11630 Model (12V) has a no-load current of only 0.01A and a stall current of just 0.30A. This is an extremely energy-efficient design, perfect for passenger car Blend Doors. Since blend doors require frequent micro-adjustments, low current means less heat generation, longer brush life, and minimal stress on the ECU’s drive chip (H-Bridge).
Low Voltage vs. High Torque: Although the 25145 Model (5V) has a lower voltage, it utilizes thicker wire and fewer turns to achieve a stall torque approaching 200 g.cm and a higher speed (5495 RPM). This design is common in systems requiring direct integration with 5V logic circuits or power supply via step-down converters.
High Voltage Advantage for Commercial Vehicles: The 10680 Model (24V) exhibits the highest stall torque (234.21 g.cm). Commercial vehicles (trucks, buses) have longer HVAC ducts, larger dampers, and tighter seals, thus requiring greater torque to overcome mechanical resistance. The 24V system allows for greater power output at lower currents (P=UI), explaining why its stall current is only 0.69A despite outputting the strongest torque.
Torque-Speed Characteristic Analysis
A typical characteristic of DC motors is that torque is inversely proportional to speed.
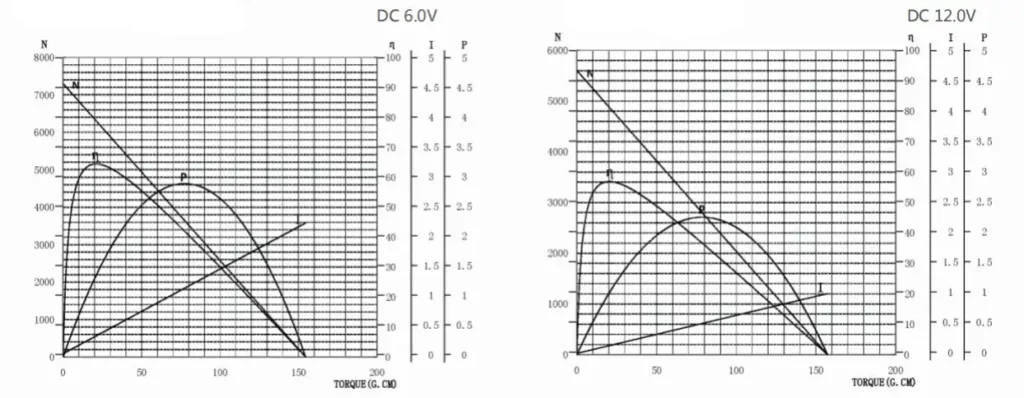
Startup and Stall:
When the damper starts from a standstill, or faces jamming due to icing or aging seals, the motor must output a force close to Stall Torque.
The TSL-RS-370 series offers a stall torque range between 95g.cm and 234g.cm.
After amplification by a 100:1 to 400:1 reduction gearbox, the final output shaft torque can reach several Newton-meters (N·m), sufficient to crush light ice or overcome mechanical sticking caused by thermal expansion and contraction.

Max Efficiency Point:
The “At Maximum Efficiency” column in the datasheet is critical. Engineers design the reduction ratio to ensure the damper’s normal operating load falls near the motor’s maximum efficiency point.
For example, for the 12V 11630 model, the optimal operating point is at 15.34 g.cm torque and 2674 RPM. Running the motor under loads far exceeding this point long-term leads to reduced efficiency, increased heat, and accelerated brush wear.
Power Density and Thermal Management
Despite the compact size of the TSL-RS-370, its peak output power at 24V can exceed 1.43W. Inside a sealed actuator housing, heat dissipation is a challenge.
12V Low Power Strategy: The low power design of the 11630 model (0.42W output) is clearly intended to manage heat accumulation. It sacrifices some torque in exchange for extremely low heat generation, which is vital for blend doors that are in a “holding” state or making frequent micro-movements for long periods.
S2 Duty Cycle: Most damper actuators are designed for short-time duty. For instance, an intake door only needs to run for a few seconds to complete a switch. Therefore, high power density models like the 5V and 24V versions complete their action before reaching thermal saturation, despite heating up faster.
Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering Design of Damper Actuators
The TSL-RS-370 motor is merely the power source; achieving precise damper control relies on precision mechanical transmission and mechatronic integration.
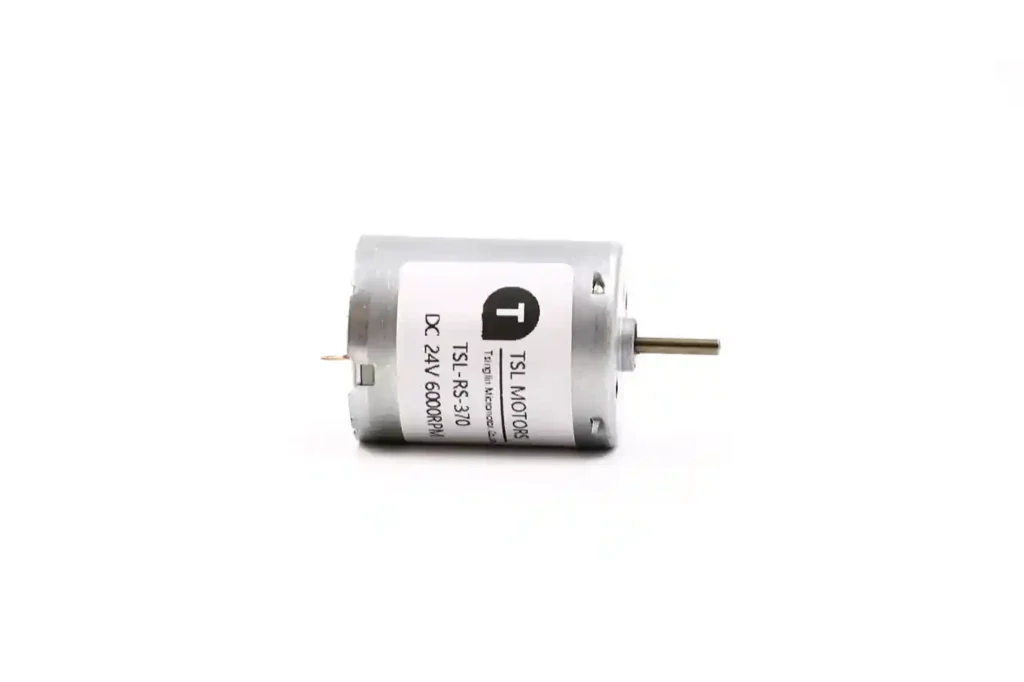

Reduction Mechanism Design
Since motor speeds reach thousands of RPM (e.g., the 20140 model reaches 7300 RPM), while full-travel damper movement typically takes 3-8 seconds, the reduction mechanism is crucial.
Multi-stage Gear Transmission: A multi-stage reduction scheme using a worm (connected to the motor shaft) driving helical or spur gears is typically employed. The total reduction ratio is usually between 300:1 and 600:1.


Noise Suppression: While worm drives have lower efficiency, they offer smooth operation and low noise. They also naturally possess “self-locking” functionality to prevent wind pressure from pushing the damper back. Gear materials often use Polyoxymethylene (POM) or oil-impregnated nylon, utilizing the material’s self-lubricating and shock-absorbing properties to reduce mechanical noise during high-speed operation of the TSL-RS-370.
Grease Selection: The grease filled inside the actuator must not solidify at -40°C (to guarantee low-temperature starting torque) and must not run or leak at +85°C (to prevent contamination of motor brushes).
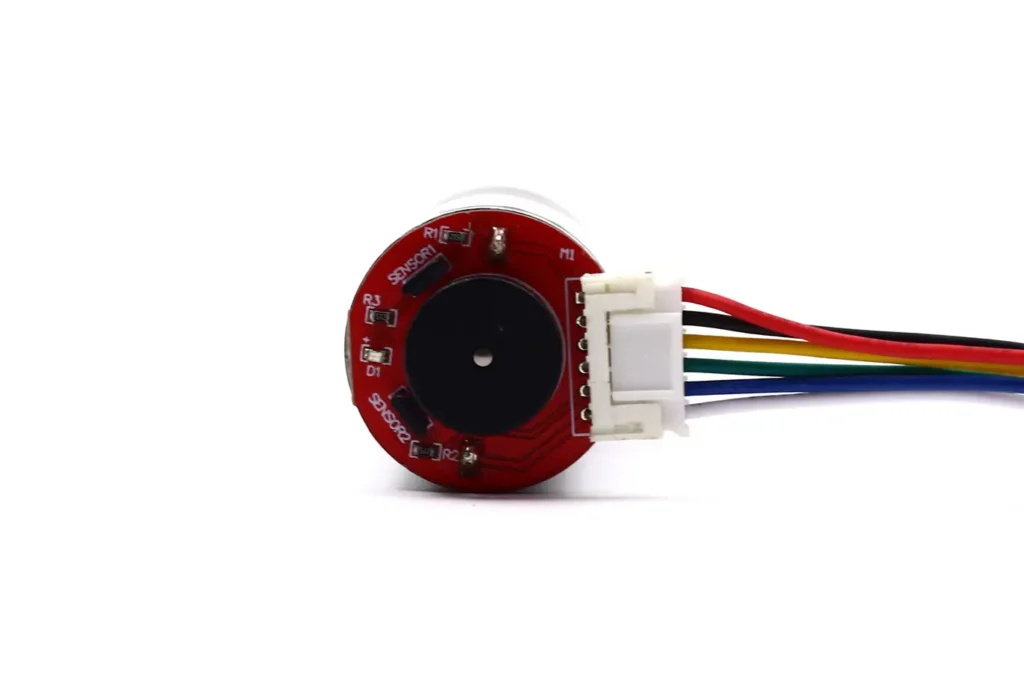
Position Feedback Sensors
To achieve closed-loop control, the actuator output shaft is usually connected to a Potentiometer.
Mechanism: As the output shaft rotates, the potentiometer outputs a voltage signal linearly proportional to the angle (typically 0-5V). The ECU reads this voltage, compares it with the target value (PID control), and drives the TSL-RS-370 motor forward or backward to eliminate the error.

Carbon Film Wear: This is a primary failure mode. If the high torque of the TSL-RS-370 is paired with a rough control algorithm (frequent dithering), it accelerates the wear of the potentiometer’s carbon film, leading to signal loss at specific positions (Dead Spots) and triggering system fault codes.
Structural Integration
Modern actuator designs trend towards high integration. The TSL-RS-370 motor is often soldered directly onto the control PCB, with the potentiometer and connectors injection-molded into the housing. This design reduces wiring connections and improves vibration resistance, though it means the entire assembly must be replaced if the motor or sensor fails.

Drive and Control Strategies: From Open Loop to Smart Closed Loop
The motor is just the executor; the control algorithm is the soul. Control strategies for the TSL-RS-370 have evolved from simple switch control to complex bus control.
Basic H-Bridge Drive
This is the most common control method. The ECU contains an H-bridge circuit composed of four power transistors (MOSFETs).
- Forward: Q1 and Q4 conduct; current flows from positive to negative.
- Reverse: Q2 and Q3 conduct; current flows inversely.
- Braking: Lower bridge arms Q3 and Q4 conduct simultaneously, utilizing the motor’s back EMF to generate braking torque and prevent Overshoot.
For the 12V 11630 model, the stall current is only 0.3A, allowing the use of low-cost integrated drive chips. In contrast, the 5V 25145 model, with a stall current of 2.47A, requires higher-power discrete MOSFETs.
PWM Speed Regulation and Soft Start
To reduce noise and mechanical shock, modern HVAC controllers use Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) for the TSL-RS-370.

- Soft Start: At startup, the duty cycle gradually increases from 0% to 100%, avoiding the gear clash and current surge caused by sudden motor acceleration.
- Soft Stop: Approaching the target position, the PWM duty cycle is reduced to decelerate the motor, improving positioning accuracy and preventing the damper from slamming into the limit stops.
LIN Bus Smart Actuators
In high-end vehicles, direct drive is being replaced by the LIN (Local Interconnect Network) bus.
- Distributed Control: Each actuator integrates a Microcontroller (MCU) and LIN transceiver. The TSL-RS-370 motor is driven directly by chips inside the actuator.
- Advantages: The HVAC main control unit sends digital commands (e.g., “Move to 50% position”) via a single signal wire, and the actuator performs self-closed-loop control. This greatly reduces vehicle wiring weight and complexity.
- Self-Diagnosis: Smart actuators can monitor the running current of the TSL-RS-370. If the current is abnormally high (damper jammed) or low (gear broken), the actuator reports specific fault codes (e.g., B11F0) to the main unit via the LIN bus, greatly facilitating repair diagnosis.
Calibration and Initialization
Due to mechanical installation tolerances and gear backlash, the ECU must “learn” the physical limit positions of the damper.
- Homing Procedure: The ECU commands the motor to move in one direction until a sharp rise in current is detected (Stall). At this point, the TSL-RS-370 current reaches the Stall Current in the datasheet (e.g., 0.3A for the 11630 model). The ECU captures this peak, designates it as the physical endpoint, records the potentiometer voltage, and repeats the process in the reverse direction.
- Importance: If a motor or actuator is replaced without performing this procedure, it can lead to improper damper sealing (air leaks) or continuous motor stalling and overheating.
NVH Characteristics and Acoustic Engineering
In the era of electric vehicles, without engine noise to mask it, HVAC actuator noise becomes particularly obtrusive. The acoustic design of the TSL-RS-370 is one of its core competitive strengths.
Noise Source Analysis
Brush Friction: The sound of carbon brushes rubbing against the commutator. Carbon brushes have longer life but higher friction coefficients than metal brushes, resulting in slightly more noise. Based on customer requirements, we can use precious metal brushes or optimized carbon materials to reduce friction noise.
Bearing Noise: If Sleeve Bearings lack oil or precision, they generate a “whirring” sound at high speeds due to axial play. We utilize high-quality imported Japanese bearings to ensure lower noise levels.
Cogging Torque: Magnetic resistance fluctuations felt by the rotor spinning in the magnetic field cause uneven operation and low-frequency vibration. Optimized Skewed Slot Rotor designs can significantly reduce this effect.
Acoustic Optimization Strategies
Vibration Isolation: Actuators are typically connected to the HVAC housing via rubber grommets to isolate motor vibration from transferring to the box (Structure-borne noise).
Housing Reinforcement: Thickening the actuator shell and adding ribs increases rigidity, avoiding resonance with the specific frequencies of the TSL-RS-370.
Reliability Engineering and Failure Mode Analysis
Common Failure Modes
Gear Stripping: The most common source of “clicking” sounds. While labeled a motor failure, it is often due to the damper physically jamming (e.g., sticky seals, foreign objects), causing the TSL-RS-370 to output maximum stall torque, exceeding the yield strength of the nylon gears. The high torque of the 24V model (10680) makes it more prone to damaging downstream plastic gears.
Brush Wear and Carbon Buildup: Long-term use generates carbon dust that accumulates between commutator slots, leading to short circuits or poor contact. This is common in frequently adjusted blend door motors.
TIP:To extend the lifespan of the 370 motor, we developed a version with extended carbon brushes and wet-pressed magnets.Meanwhile, the carbon brushes are replaceable.

Thermal Failure: If the ECU’s over-current protection logic fails and the motor stalls for extended periods, winding temperatures rise rapidly, melting insulation varnish, shorting turns, and eventually burning out the motor or drive circuit.
Position Sensor Drift: Potentiometer wear causes voltage jumps, leading the ECU to misjudge position and drive the motor back and forth (“Hunting”), causing continuous adjustment noise.
Preventive Maintenance and Diagnosis
Cabin Filter Replacement: A clogged filter increases intake resistance, significantly increasing the load on intake and mode actuators, accelerating TSL-RS-370 wear.
Auditory Diagnosis:
Clicking/Cracking: Broken gear teeth.
Humming but no airflow change: Motor spinning freely (internal shaft broken) or motor stalled.
Silence: Motor open circuit, blown fuse, or ECU fault.
Evolution in New Energy Vehicle Thermal Management: From Comfort to Survival
With the proliferation of New Energy Vehicles (NEVs), the functional boundaries of damper actuators are expanding.

Fusion with Battery Thermal Management Systems
In EVs, the HVAC system serves not only the passengers but also the high-voltage battery.
- Chiller Control: Many EVs use AC refrigerant to cool battery coolant. This requires precision dampers to control airflow through front condensers and internal evaporators, balancing cabin cooling with battery cooling needs.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs are extremely sensitive to energy consumption. The TSL-RS-370CHV-11630 model’s low power characteristics (0.01A no-load, 0.05A at max efficiency) make it an ideal choice for EV thermal management, helping to extend driving range.
Smart Cockpit and Active Regulation
- Tunnel Mode: Combining GPS and cloud data, the vehicle automatically commands the TSL-RS-370 to close the intake damper before entering a tunnel to block pollution.
- Sun Tracking: Using visual sensors to track sunlight angles, the system independently adjusts driver and passenger blend doors for human-centric zoned temperature control.
- Pre-conditioning: Remote starting of the AC via mobile app before the owner enters the vehicle.
Conclusion
Automotive HVAC damper actuators and their core component, the TSL-RS-370 motor, though hidden deep within the dashboard, are key to guaranteeing the comfort, safety, and energy efficiency of modern vehicles.
Their customized design across different voltage platforms achieves a balance between efficiency and performance, translating into the quiet and comfortable experience perceived by users through precision mechanical coupling and intelligent control algorithms.
In the future, as the automobile evolves into a “Third Living Space,” damper actuators will become more intelligent and efficient. The TSL-RS-370 series motors will continue to play an irreplaceable role in the thermal management of new energy and smart vehicles.
As a leading Chinese DC motor manufacturer, we are committed to providing one-stop customized solutions, driving industry upgrades with reliable products and deep engineering expertise.
FAQ
Q1: Which HVAC dampers are suitable for the TSL-RS-370?
A: It fits all key types: Intake actuators (Recirculation), Blend doors (Temp mixing), and Mode actuators (Air distribution).
Q2:What control methods does the TSL-RS-370 support?
A: It fully supports PWM speed regulation, LIN bus smart control, and potentiometer-based closed-loop feedback.
Q3: Is it durable enough for frequently moving Blend Doors?
A: Yes. We optimized the brush materials specifically for frequent micro-adjustments and stop-start cycles.
Q4: Is this motor suitable for Electric Vehicles (EVs)?
A: Absolutely. Its low static current and high efficiency help save battery power and extend EV range.
TSL-Motor: Custom Motor Solutions
Established in 2009, TSL Motor has evolved into a leading innovator in precision drive systems and specialized motor manufacturing. Our 15,000㎡ advanced production facility in Shenzhen houses a skilled workforce of 200+ professionals, delivering an annual output of 2 million units to global markets.
Continuous R&D investment in energy-efficient motor technologies
Lean manufacturing processes ensuring cost-competitive pricing
Agile production capacity scaling for batch customization
Global compliance certifications (CE, RoHS, REACH)
With dual focus on operational excellence and client success, Twin Motor empowers businesses worldwide to achieve technological differentiation. Our engineering team welcomes complex challenges across automotive, robotics, and smart infrastructure applications.
Contact our solutions center to discuss your project requirements or request our technical portfolio.

24mm Micro DC Motor – 30mm Type Model TSL-RS-370
♦ Basic Info:
- Brand:TSL
- Origin:China
- Motor Model:TSL-RS-370
- #More Specifications
♦ Typical Applications:
- Audiovisual equipment: CD Player / VCR
- Home Appliances:Kitchen Appliance / Blood Pressure Meter
- Automotive products: air conditioning fan regulator




