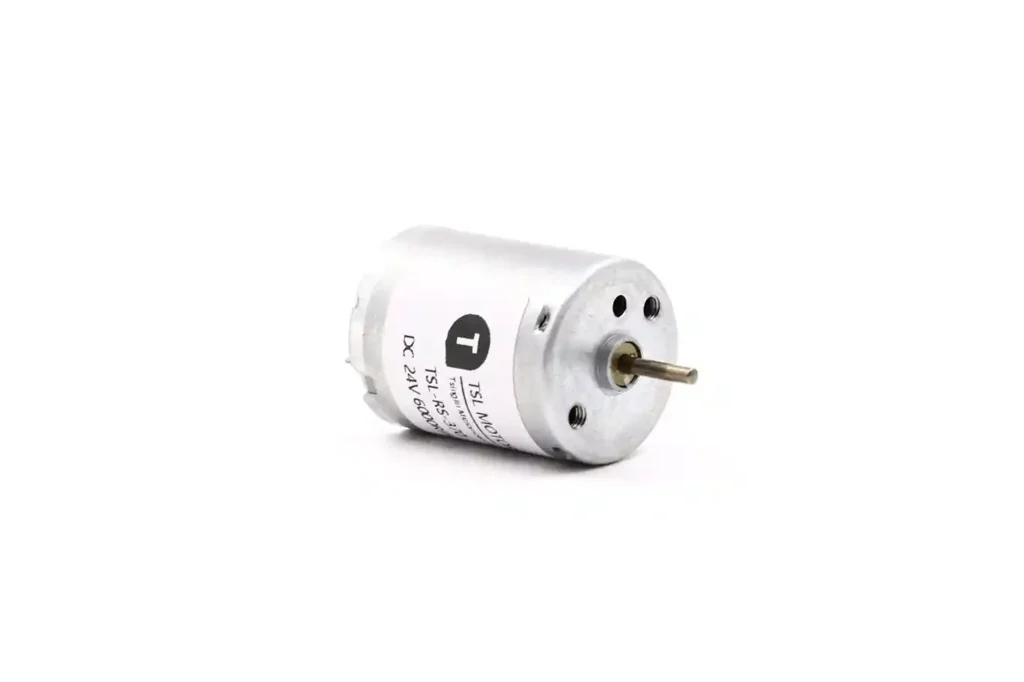
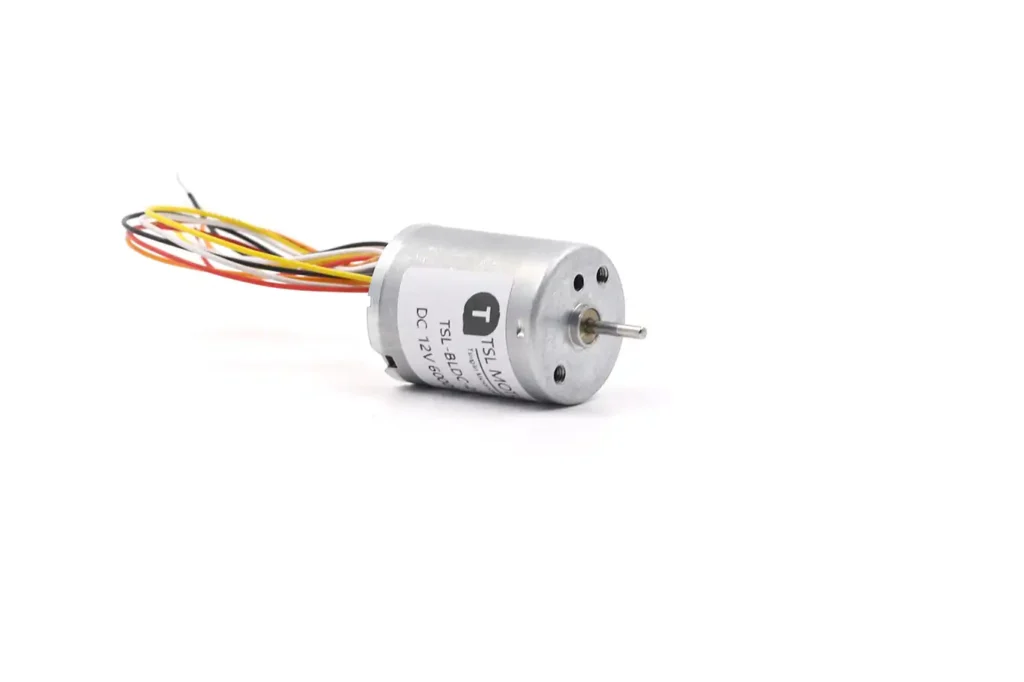
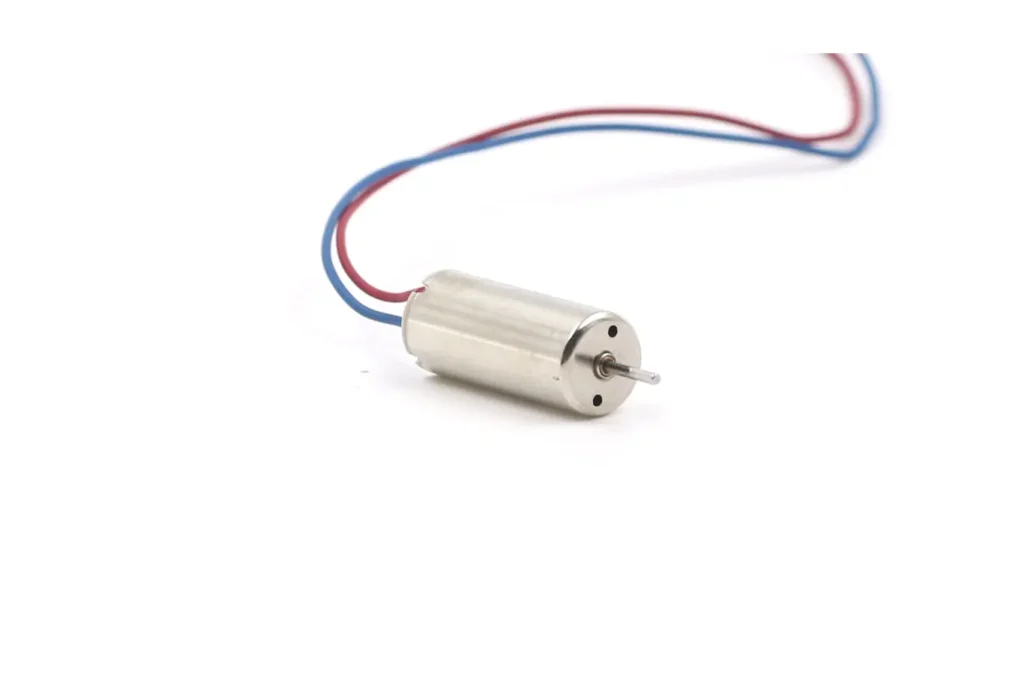
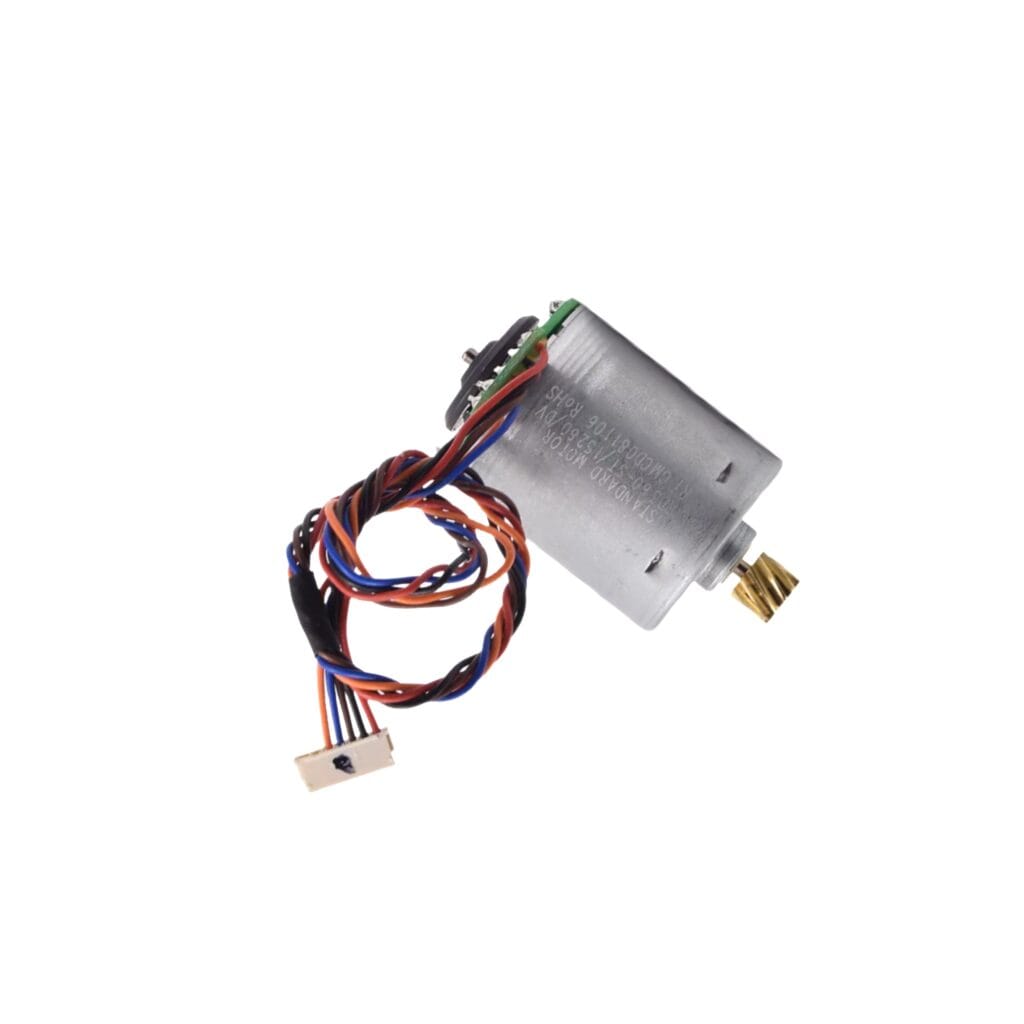
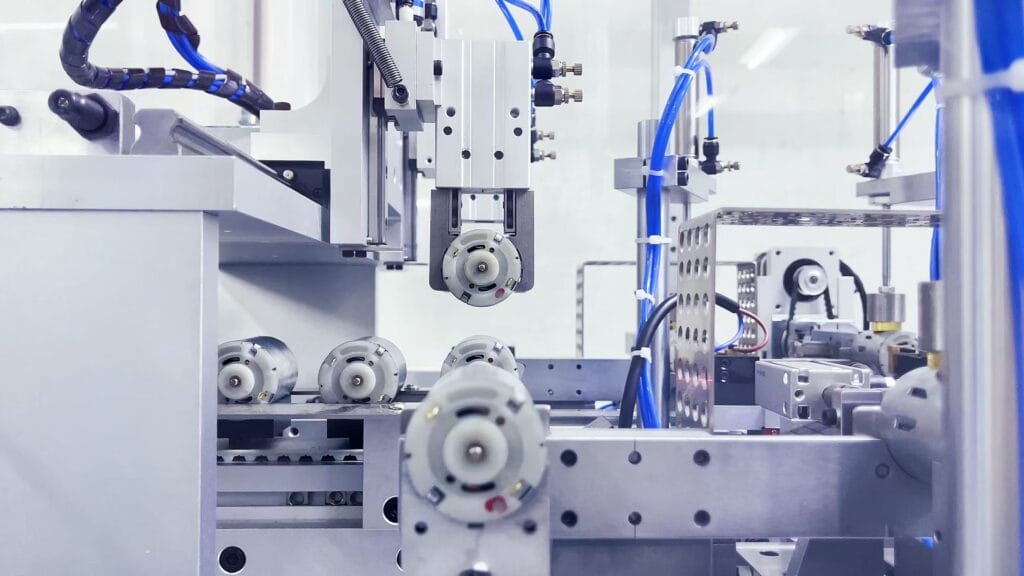
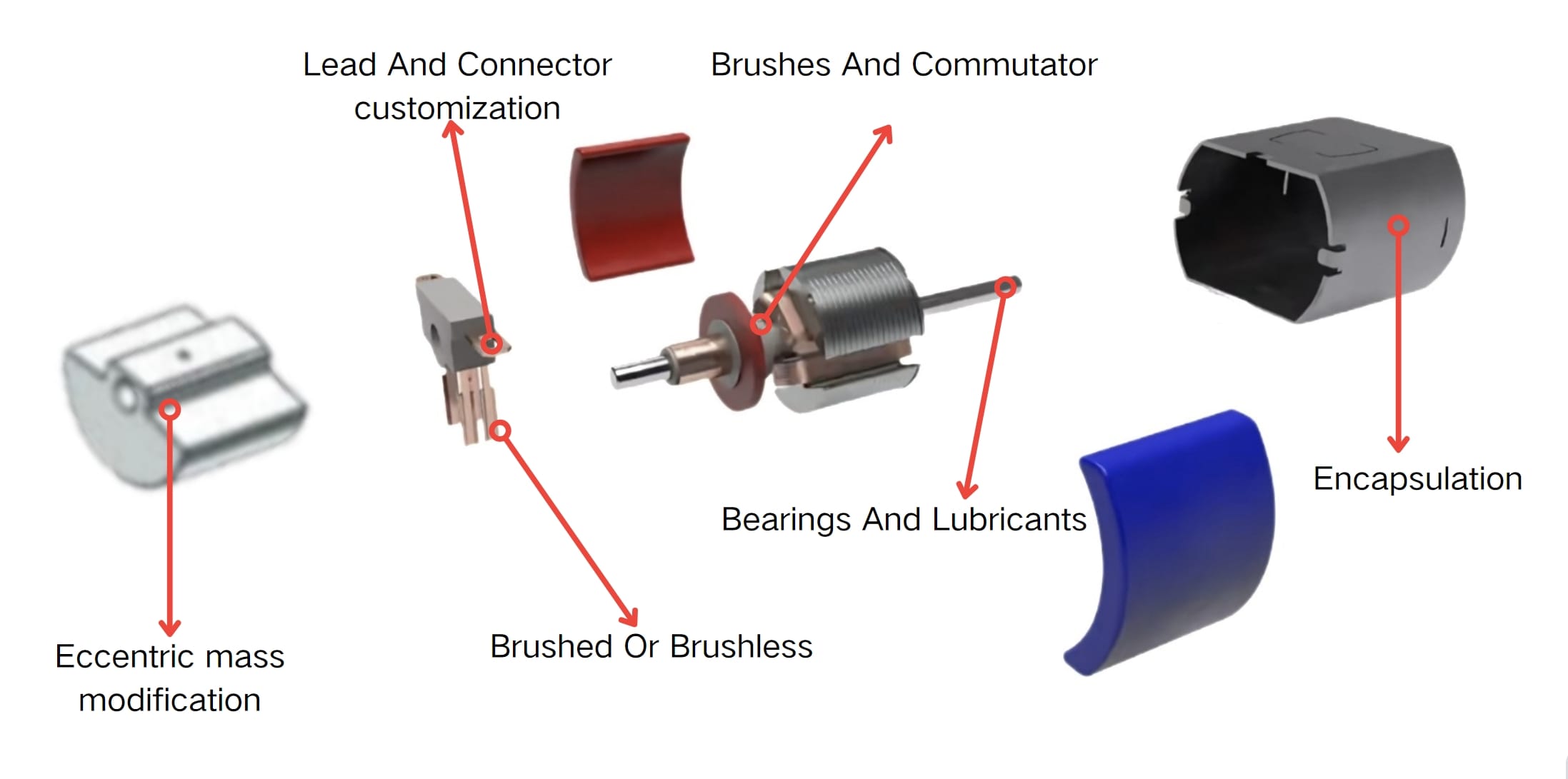
Coreless brushed DC motors provide better performance compared to iron core motors, though they come at a higher cost.
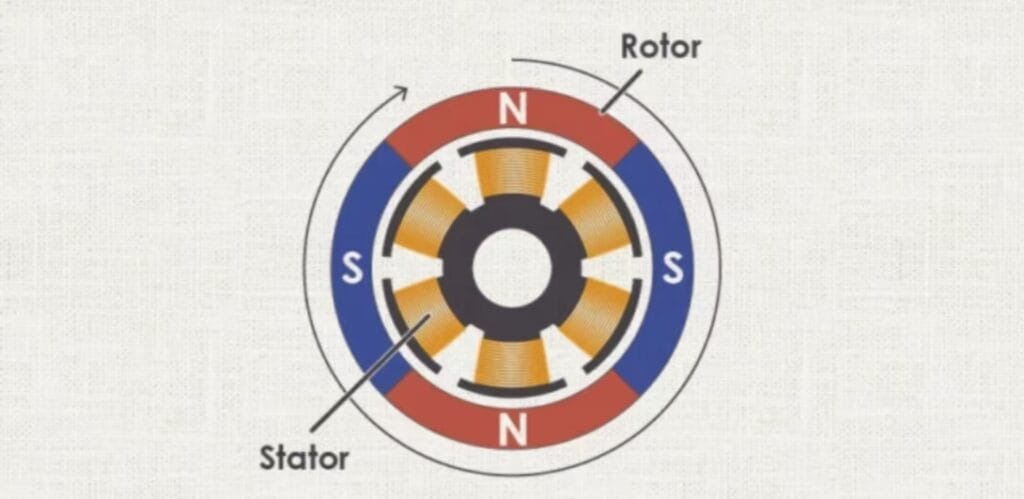
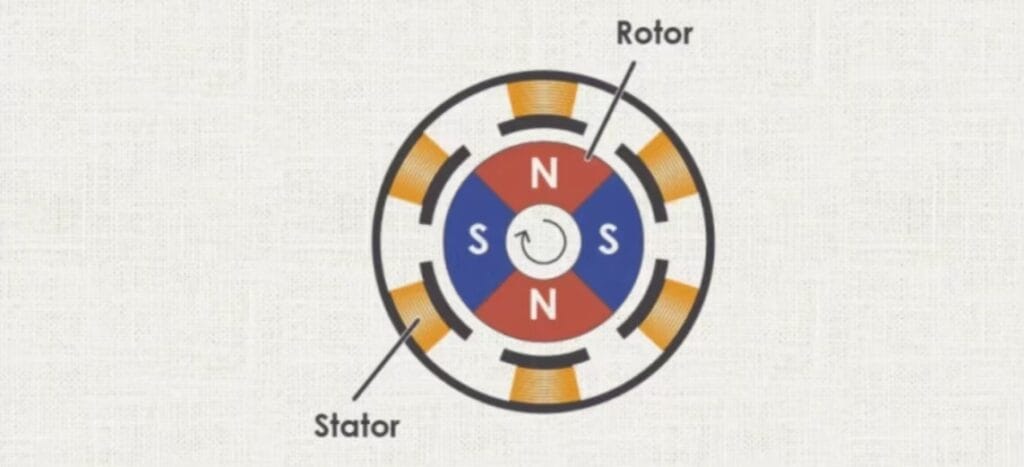
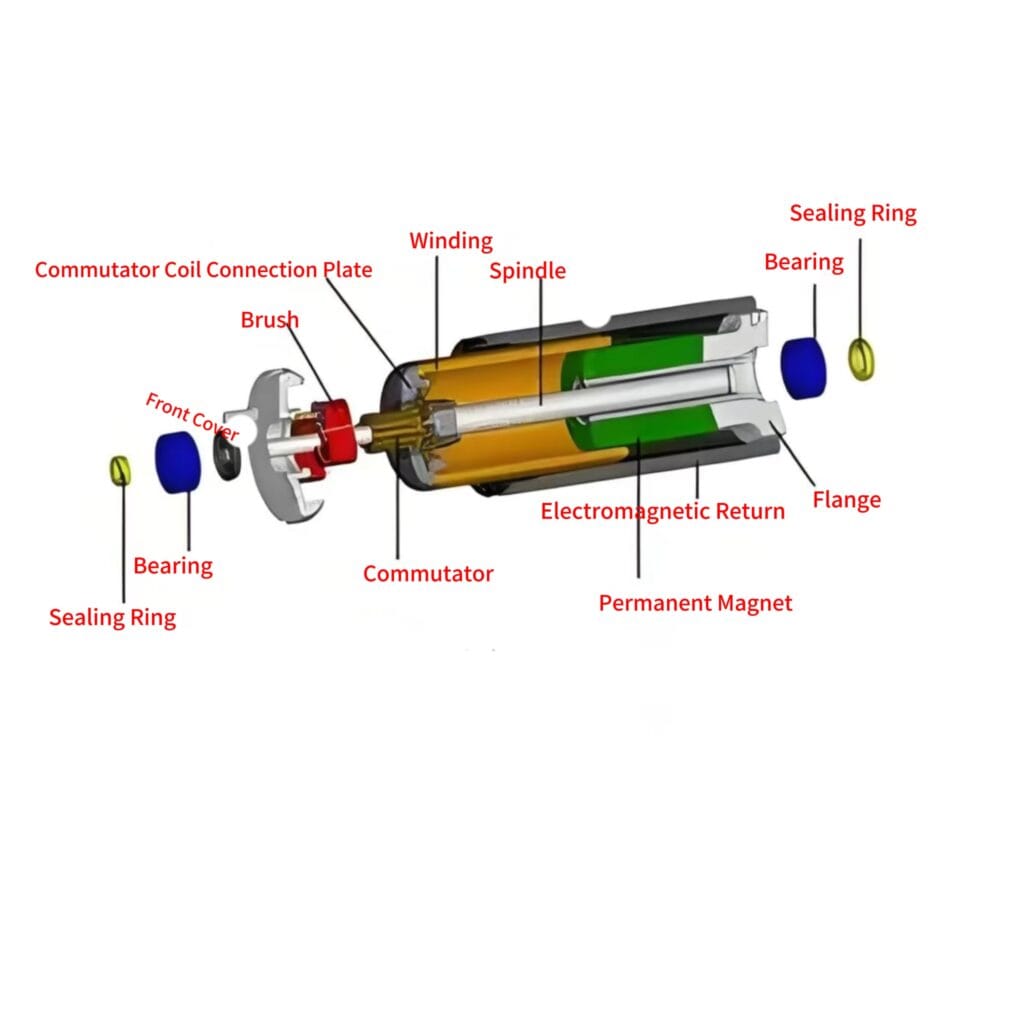
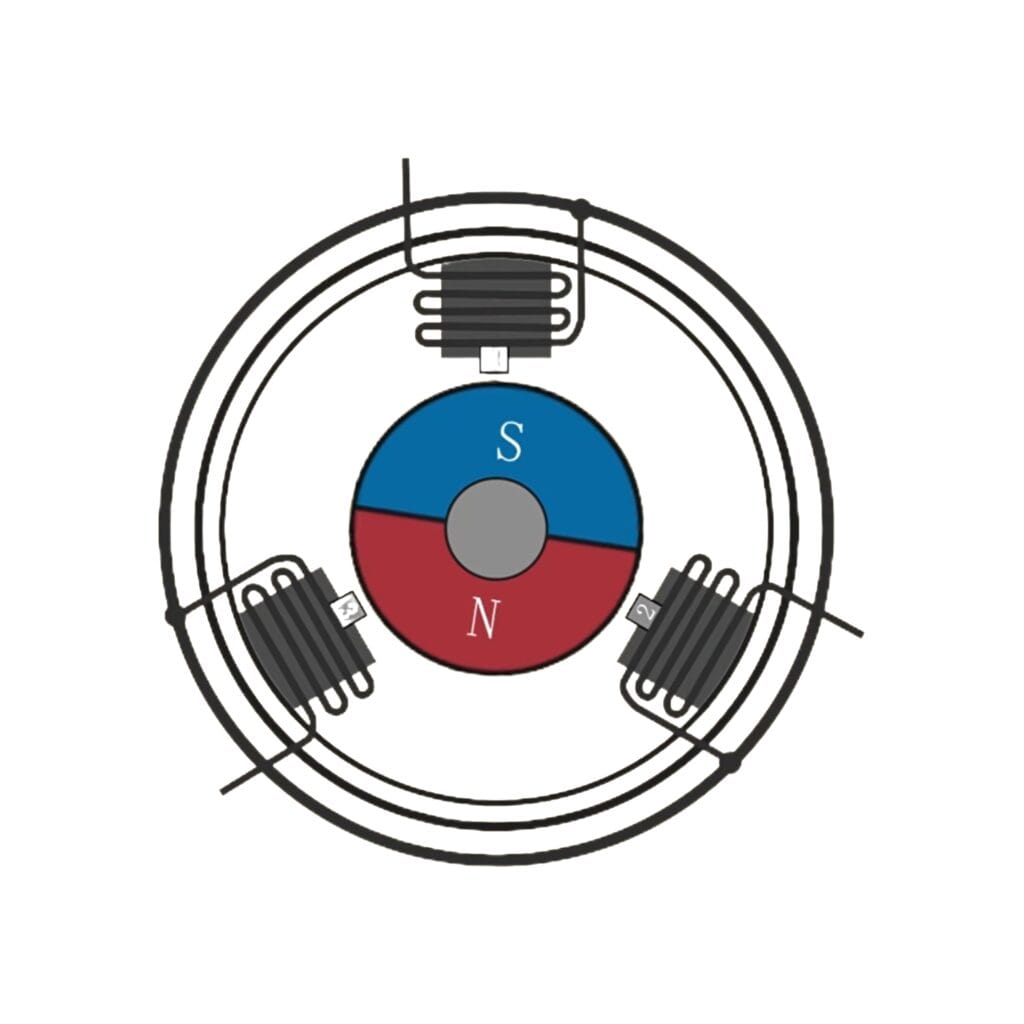
In this design, the motor features a stationary high-performance toroidal magnet instead of a traditional winding. The motor’s windings are mounted on the shaft and placed in a resin mould, rotating around the magnetic core. This setup improves efficiency by reducing magnetic losses. Additionally, the proximity of the windings to the motor case helps dissipate heat more effectively, allowing for higher power output.
Like iron core motors, coreless motors use mechanical commutation through brushes, enabling them to run on a simple DC voltage. Positive voltage drives the motor forward, and negative reverses the direction.
Coreless motors are ideal for two main applications: motors with a diameter under 10mm, where this design is the only option for adequate performance, and larger motors where high performance is needed and DC voltage is preferred over the more complex signals used by brushless motors.
We commonly use coreless motors in compact, high-performance applications, as well as in lower volume industrial, instrument, and medical device.